Understanding Flat Head Syndrome
This refers to head flattening on one side of the head (Plagiocephaly), or to the back of the head (Brachycephaly), which can be caused by pressure on one area of the infant's head over time, as well as other factors.
Plagiocephaly, or Flat Head Syndrome, has recently received increased attention in pediatric neurosurgical and craniofacial surgeons.
Asymmetry is rarely caused by brain malformation or a unilateral fused skull, but usually results from late gestational or postnatal deformation. An increase in positional head deformities has been reported, since the recommendation of supine sleeping to reduce the likelihood of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS).
Plagiocephaly, or Flat Head Syndrome, has recently received increased attention in pediatric neurosurgical and craniofacial surgeons.
Asymmetry is rarely caused by brain malformation or a unilateral fused skull, but usually results from late gestational or postnatal deformation. An increase in positional head deformities has been reported, since the recommendation of supine sleeping to reduce the likelihood of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS).
Understanding Plagiocephaly
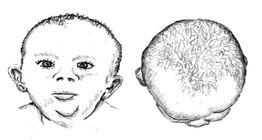
When an infant's rapidly growing head is maintained in a nearly fixed position against the uterine wall, or in postnatal cases, against a mattress, the calverium is progressively flattened. Such deformational plagiocephaly will generally improve within a few months after birth, especially if a full range of neck movement can be achieved rapidly.
Although undetermined, the incidence of plagiocephaly often quoted is one in every 300 births, and perhaps 10% of affected infant's plagiocephaly may develop into a permanent mild-to-severe deformity.
Although undetermined, the incidence of plagiocephaly often quoted is one in every 300 births, and perhaps 10% of affected infant's plagiocephaly may develop into a permanent mild-to-severe deformity.
Understanding Brachycephaly
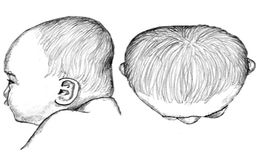
Brachycephaly is a condition where the head is disproportionately wide compared to its depth, caused by prolonged positioning on the back of the head. This results in a head shape that is very wide and short.
The Therapeutic Helmet
If the pressure of the rapidly growing brain against a flat surface would flatten the head, then the pressure against a concave surface should round the head back again.
The philosophy behind the therapeutic helmet is to achieve the maximum correction during the early growth period.
The brain and the skull grow very quickly during the first year of life. The growth rate is quite steep in the early months, and then begins to level off after six months of age. In this new therapeutic helmet design, increased importance is emphasized on biomechanical and ergonomic principles.
Eighty-five percent of postnatal skull growth occurs during the first year of life. Therefore, the sooner the mechanical treatment is instituted, and the more aggressive the treatment is, the better the result will be.
The philosophy behind the therapeutic helmet is to achieve the maximum correction during the early growth period.
The brain and the skull grow very quickly during the first year of life. The growth rate is quite steep in the early months, and then begins to level off after six months of age. In this new therapeutic helmet design, increased importance is emphasized on biomechanical and ergonomic principles.
Eighty-five percent of postnatal skull growth occurs during the first year of life. Therefore, the sooner the mechanical treatment is instituted, and the more aggressive the treatment is, the better the result will be.

